NIH scientists use artificial intelligence to improve next-generation imaging of cells in the back of the eye.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health applied artificial intelligence (AI) to a technique that produces high-resolution images of cells in the eye. They report that with AI, imaging is 100 times faster and improves image contrast 3.5-fold. The advance, they say, will provide researchers with a better tool to evaluate age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other retinal diseases.
“Artificial intelligence helps overcome a key limitation of imaging cells in the retina, which is time,” said Johnny Tam, Ph.D., who leads the Clinical and Translational Imaging Section at NIH’s National Eye Institute.
Table of Contents
AI DEEP LEARNING ALGORITHM
PARALLEL DISCRIMINATOR
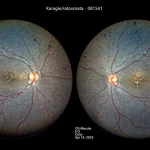
To address this, the researchers developed a deep learning algorithm called the Parallel Discriminator Generative Adversarial Network (P-GAN). P-GAN effectively de-speckles AO-OCT images, enabling clearer visualization of retinal cells, particularly the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), which is crucial in many retinal diseases. This AI-driven approach reduces the need for multiple image captures and extensive post-processing, thus significantly speeding up the imaging process.
What AI is doing faster:
Automated image analysis
AI can instantly identify signs of diseases like diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, or age-related macular degeneration, which would otherwise require a specialist to analyze.
Segmentation and labeling
AI can rapidly segment retinal layers or highlight lesions, a task that would take clinicians several minutes per image.
Triage and prioritization
AI can help flag urgent cases in massive datasets almost instantly.
Reporting
Automatically generates diagnostic reports.
Compared to:
⦁ Manual review by ophthalmologists or trained technicians, which can take 5–10 minutes per image depending on complexity, AI can often perform similar tasks in under a second—leading to the “100x faster” claim.
Real-world impact
⦁ Faster screenings in large-scale eye care programs.
⦁ Early detection in underserved or rural areas using portable devices plus AI.
⦁ Reduced workload on human experts.
Clinical Implications
The enhanced speed and clarity of retinal imaging have several potential benefits.
Early Detection
Improved imaging can facilitate the early diagnosis of retinal diseases like AMD, potentially leading to better patient outcomes.
Increased Accessibility
Faster imaging processes can make advanced retinal diagnostics more accessible, especially in underserved or rural areas.
Reduced Clinician Workload
Automation of image processing can alleviate the burden on ophthalmologists, allowing them to focus more on patient care.
RCEENetworks proudly presents RetinaWise AI — a cutting-edge, cloud-based solution developed in alignment with NIH research.
Streamline your optometry workflow with the power of AI.
Enjoy a free one-month subscription and experience the future of retinal diagnostics today. Contact us right now.